Reading-Notes
Code Fellows Python 401
Read: 06 - Ten Thousand Game 1
How to use Random Module
- will allow you to produce random numbers
Randint
- accepts two parameters: generates an integer between 2 number.
import random print random.randint(0, 5)output either 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5
Random
- a random number between 0 and 1: can be multiplyed to produce larger numbers.
import random random.random() * 100output will be between 0 and 100
Choice
- Generate a random value from the sequence sequence. ``` python import random random.choice( [‘red’, ‘black’, ‘green’] )
myList = [2, 109, False, 10, “Lorem”, 482, “Ipsum”] random.choice(myList)
### Shuffle
- shuffles the elements in a list in place
``` python
from random import shuffle
x = [[i] for i in range(10)]
shuffle(x)
output: print x gives
[[9], [2], [7], [0], [4], [5], [3], [1], [8], [6]]results will vary
Randrange
- Generate a randomly selected element from range(start, stop, step)
random.randrange(start, stop[, step]) import random for i in range(3): print random.randrange(0, 101, 5)
Code Example
import random
import itertools
outcomes = { 'heads':0,
'tails':0,
}
sides = outcomes.keys()
for i in range(10000):
outcomes[ random.choice(sides) ] += 1
print 'Heads:', outcomes['heads']
print 'Tails:', outcomes['tails']
What is Risk Analysis
In Software Testing, risk analysis is the process of identifying the risks in applications or software that you built and prioritizing them to test.
Why
- highlights potential problems
mitigate risk by practicing problem prevention:
- Conduct Risk Assessment review meeting
- Use maximum resources to work on high-risk areas
- Create a Risk Assessment database for future use
- Identify and notice the risk magnitude indicators: high, medium, low.
unavoidable risks:
- The time that you allocated for testing
- A defect leakage due to the complexity or size of the application
- Urgency from the clients to deliver the project
- Incomplete requirements
levels of risk:
- High: non-tolerable. The company might face loss.
- Medium: not desirable. The company may suffer financially but there is a limited risk.
- Low: tolerable. little or no external exposure or no financial loss.
Risk Identifications:
-
Business Risks: This risk is the most common risk associated with our topic. It is the risk that may come from your company or your customer, not from your project.
-
Testing Risks: You should be well acquainted with the platform you are working on, along with the software testing tools being used.
-
Premature Release Risk: a fair amount of knowledge to analyze the risk associated with releasing unsatisfactory or untested software is required
-
Software Risks: You should be well versed with the risks associated with the software development process.
Risk Assessment
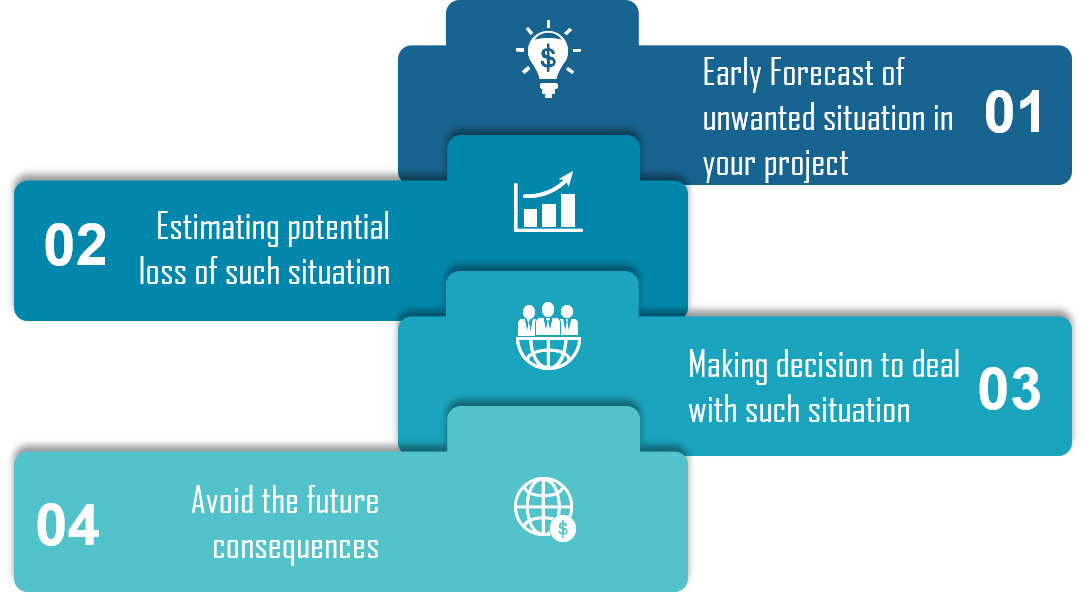
perspective of Risk Assessment
-
Effect – To assess risk by Effect. In case you identify a condition, event or action and try to determine its impact.
-
Cause – To assess risk by Cause is opposite of by Effect. Initialize scanning the problem and reach to the point that could be the most probable reason behind that.
-
Likelihood – To assess risk by Likelihood is to say that there is a probability that a requirement won’t be satisfied.
How to perform Risk Analysis
-
Searching the risk
-
Analyzing the impact of each individual risk
-
Measures for the risk identified
Test Coverage
also called code coverage
- finds untested parts of a codebase
- use things like TDD