Reading-Notes
Code Fellows Python 401
Read: Data Structure and Analysis - Trees
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees, and K-ary Trees.
Common Terminology:
Node - A Tree node is a component which may contain its own values, and references to other nodes
Root - The root is the node at the beginning of the tree
K - A number that specifies the maximum number of children any node may have in a k-ary tree. In a binary tree, k = 2.
Left - A reference to one child node, in a binary tree
Right - A reference to the other child node, in a binary tree
Edge - The edge in a tree is the link between a parent and child node
Leaf - A leaf is a node that does not have any children
Height - The height of a tree is the number of edges from the root to the furthest leaf
Traversals
how you move/navigate through a tree
- 2 types of traversal:
- Depth First
- Breadth First
Depth First
- prioritize going through the depth (height) of the tree
- dif method changes the order in which we search/print the
root - most common way to traverse through a tree is to use recursion
Pre-order: root >> left >> right
ALGORITHM preOrder(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- pre-order output of tree node's values
OUTPUT <-- root.value
if root.left is not Null
preOrder(root.left)
if root.right is not NULL
preOrder(root.right)
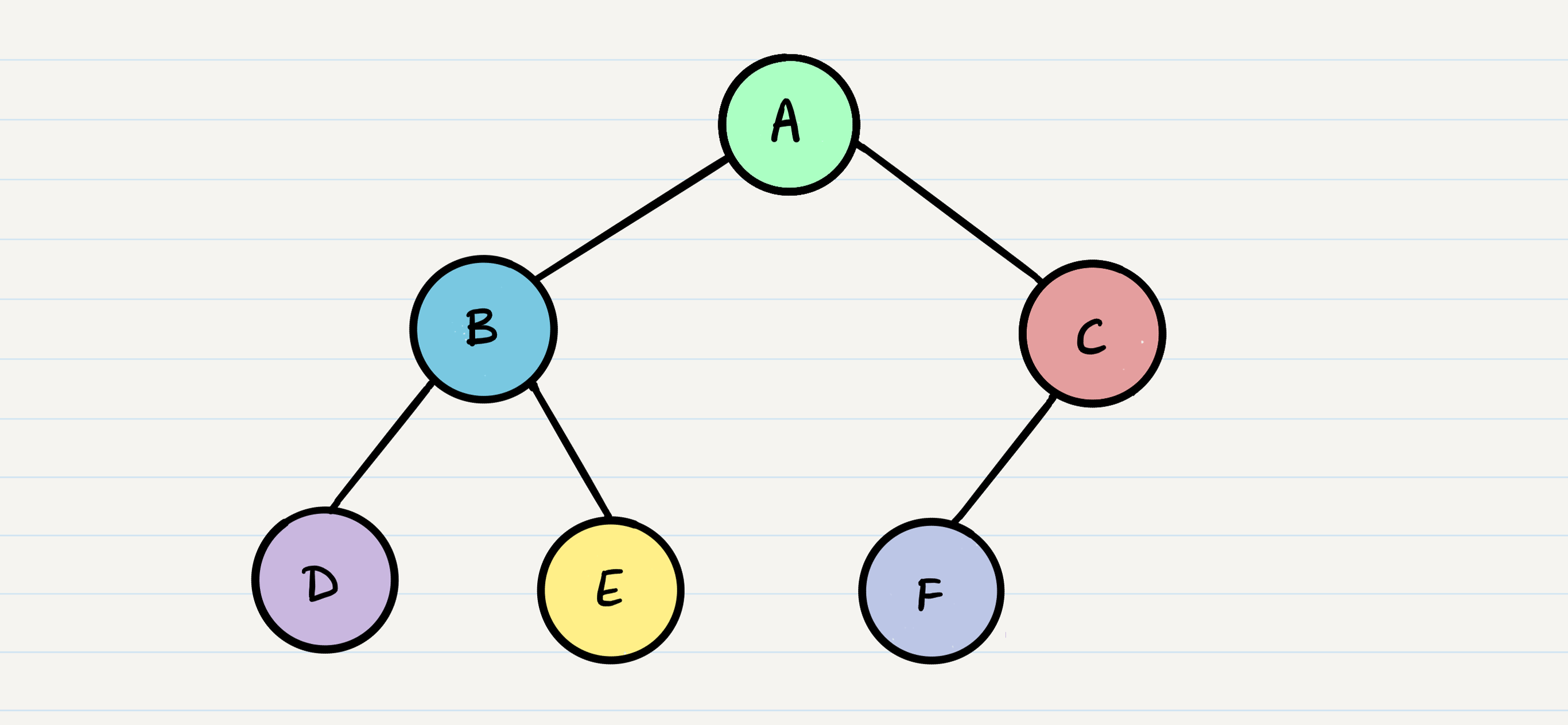
output: A, B, D, E, C, F
In-order: left >> root >> right
ALGORITHM inOrder(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- in-order output of tree node's values
if root.left is not NULL
inOrder(root.left)
OUTPUT <-- root.value
if root.right is not NULL
inOrder(root.right)
output: In-order: D, B, E, A, F, C
Post-order: left >> right >> root
ALGORITHM postOrder(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- post-order output of tree node's values
if root.left is not NULL
postOrder(root.left)
if root.right is not NULL
postOrder(root.right)
OUTPUT <-- root.value
output: Post-order: D, E, B, F, C, A
Breadth First
- iterates through the tree by going through each level of the tree
ALGORITHM breadthFirst(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- front node of queue to console
Queue breadth <-- new Queue()
breadth.enqueue(root)
while ! breadth.is_empty()
node front = breadth.dequeue()
OUTPUT <-- front.value
if front.left is not NULL
breadth.enqueue(front.left)
if front.right is not NULL
breadth.enqueue(front.right)
output: Output: A, B, C, D, E, F
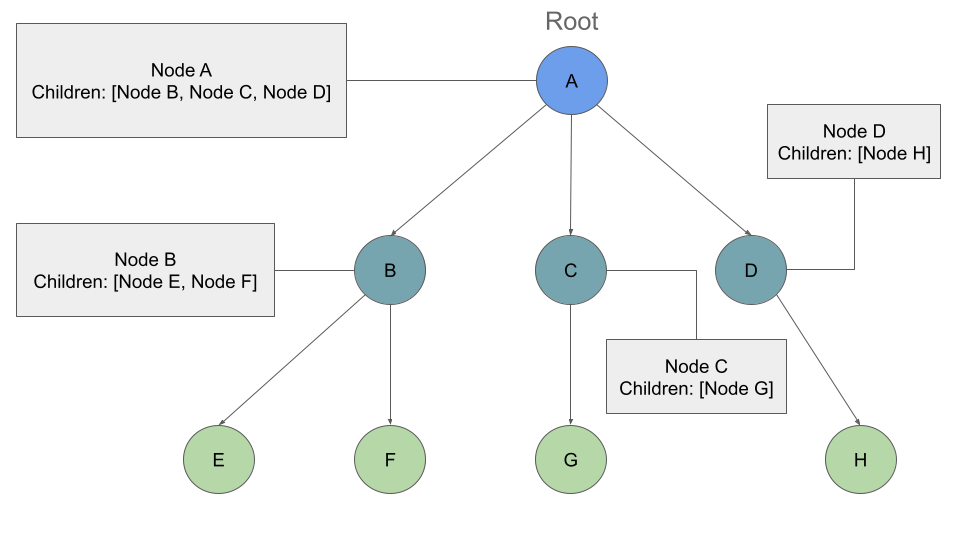
K-ary Trees
- Nodes are able have more than 2 child nodes
Krefers to the max amount of children in a K-ary Trees
Breadth First Traversal
- moving down a list of children of length k
ALGORITHM breadthFirst(root)
// INPUT <-- root node
// OUTPUT <-- front node of queue to console
Queue breadth <-- new Queue()
breadth.enqueue(root)
while ! breadth.is_empty()
node front = breadth.dequeue()
OUTPUT <-- front.value
for child in front.children
breadth.enqueue(child)
Output: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
Binary Search Trees
- all values that are smaller than the
rootare placed to the left, and all values that are larger than therootare placed to the right